How to Read Traceroute Results: A Guide for Network Novices

Traceroute is a powerful network diagnostic tool that allows you to trace the path of your data packets as they travel across the internet. It's like a road map for your data, showing each hop it makes from your computer to its final destination. Understanding how to read traceroute results is vital for troubleshooting network issues and gaining insights into a network's performance.
This guide will walk you through the basics of running traceroute, interpreting its results, and running traceroute from any global location with Globalping. Let's go!
What is Traceroute?
Traceroute is a network utility that helps you visualize the route packets of data take from your computer to a target device or server on the internet. It reveals every intermediate router or "hop" along the way, displaying vital information such as IP addresses and response times for each hop. This information is invaluable for diagnosing network issues and optimizing network performance.
Running Traceroute
Running a traceroute command is straightforward and similar to running a ping command. The basic syntax is as follows:
traceroute [options] target
target: This is the hostname or IP address of the device or server you want to trace the route to.options: These are optional parameters that allow you to customize your traceroute. For example, you can specify the number of packets to send per hop or set a maximum response timeout.
Note: If you're on Windows, use the command tracert instead!
Example: Tracing the Route to google.com
Let's say you want to trace the route from your computer to Google's website. To do this, run the following command:
traceroute google.com
This will initiate the traceroute process, and you'll see a list of hops displayed on your terminal.
Understanding Traceroute Results
Interpreting traceroute results may seem a bit daunting at first, but breaking down the information step by step makes it much more manageable. Each line in the traceroute output corresponds to a hop along the path to the target.
Here's a sample traceroute result:
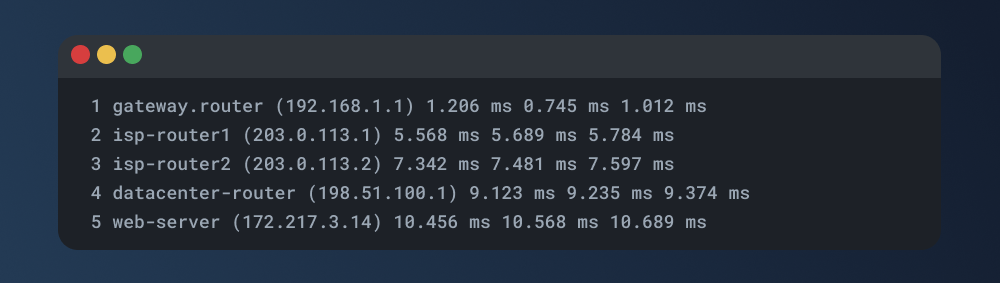
And here's what you can read from the result:
- Hop Number: The leftmost column displays the hop number, starting from 1 and increasing for each subsequent hop.
- Router IP Address (or Hostname): The second column shows the router's IP address (or hostname, if available) at each hop.
- RTT (Round-Trip Time): The next columns display the round-trip time for packets sent to that hop. You'll see three values:
- Minimum: The shortest RTT recorded for packets sent to that hop.
- Average: The average RTT over all packets sent to that hop.
- Maximum: The longest RTT recorded for packets sent to that hop.
Note: If you're on Windows, you'll see the RTTs after the hop number and the router IP address comes last.
By examining the traceroute results, you can gain valuable insights into the path your data takes to reach its destination, the response times at each hop, and potential network bottlenecks or delays.
Run traceroute from Anywhere with Globalping
Globalping allows traceroute tests (and other network measurement commands) from virtually any location worldwide. This is an invaluable resource for network enthusiasts and professionals alike, and the best part is that it's absolutely free!
How to Use Globalping for Traceroute
Leveraging the versatility of Globalping for traceroute tests is straightforward, particularly when you use our Command Line Interface (CLI) tool. To get started, visit our GitHub page and follow the step-by-step instructions for setting up the CLI tool on your machine.
Once you've successfully installed the CLI tool, you're ready to run your first traceroute! In your terminal, issue the following to initiate a traceroute from a specific location, let's say London:
globalping traceroute jsdelivr.com --from London
In this command:
- Replace "jsdelivr.com" with the domain or IP address you want to trace the route to.
- Modify the location ("London" in this case) to specify the origin of the traceroute.
Your result will resemble the familiar traceroute output we explored earlier in this article. It unveils every hop along the path, complete with IP addresses or hostnames and response times, providing you with a comprehensive picture of the route taken to your target.
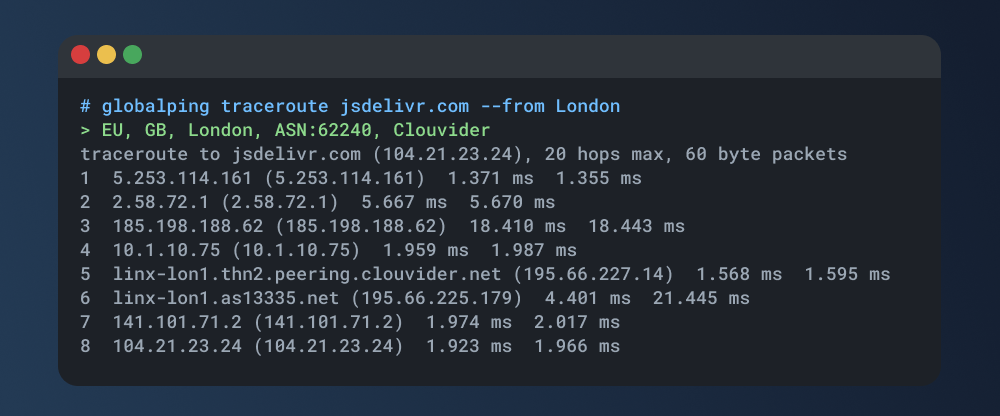
Globalping goes beyond the basics, offering advanced features and customization options for traceroute tests. With Globalping, you can trace routes from multiple locations simultaneously or specify the protocol you want to use. Check out our documentation to learn more!
Final Tips for Using Traceroute Effectively
Finally, we want to share some tips to consider when using traceroute:
- Identify Slow Hops: Pay attention to hops with unusually high RTT values. These could indicate network congestion or issues at specific points in the route.
- Check for Consistency: Look for hops with stable and consistent RTT values. Consistency is a good sign of a healthy network.
- Investigate Timeouts: If you encounter hops with asterisks (*) or timeouts, it may suggest a router that doesn't respond to traceroute requests. Often, this is normal, but it could indicate a problem.
- Analyze the Destination: The final hop in the traceroute result should be the destination server or device. Verify that the IP address or hostname matches your intended target.
- Run Multiple Traceroutes: Running traceroute from different locations or times can provide a more comprehensive view of network performance.
Conclusion
By understanding how to run a traceroute command and interpret the results, you can become adept at diagnosing network issues, optimizing routes, and ensuring smooth data transmission across the internet. Traceroute is a valuable tool for network professionals and enthusiasts alike, enabling you to explore the intricacies of the global network.
Using Globalping, you can conveniently evaluate network performance from anywhere in the world, and best of all, it’s free! Whether you're troubleshooting network issues or simply eager to explore your network's capabilities, why not give Globalping a spin today?